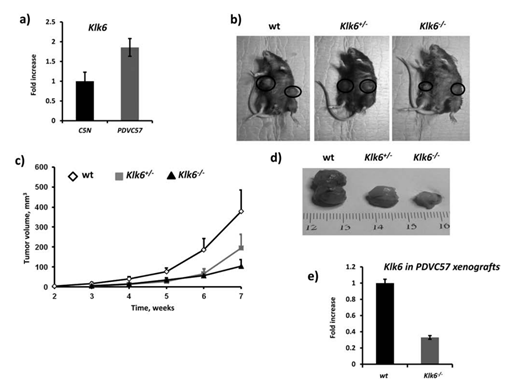
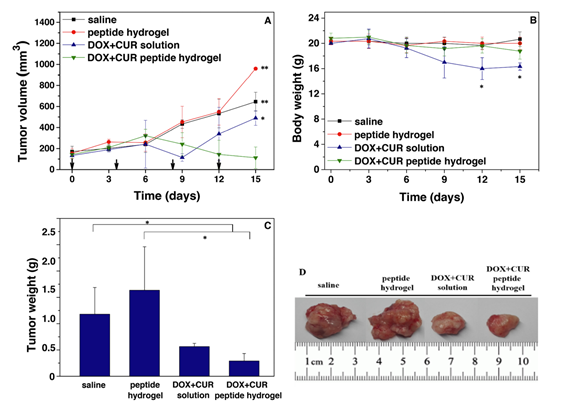
We aimed to identify and investigate prostate cancer (PCa) biomarkers which could provide a basis for the emergence of an immune signature with strong prognostic and predictive value. Our targets were to analyze IFNγ/TGFβ and TCRVβ gene expression by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS).
Major outcomes include
- IL-8 was found to be significantly upregulated in patients with metastatic and advanced PCa, whereas TGFβ was upregulated in patients with indolent or slow progressing disease. Therefore, IL-8 and TGFβ could be used as biomarkers of disease progression and for the appropriate stratification of patients to risk groups.
- Investigation of radiotherapy-induced changes in TCRVβ repertoire: the number of new TCR clones seemed to increase in the peripheral blood of PCa patients following radiation therapy, suggesting an increase in the number of released antigens (neo-antigens) into the circulation form radiation-destroyed cancer cells; these could potentially serve as tools to elicit specific immune responses and for the development of precision-orientated therapeutic approaches.
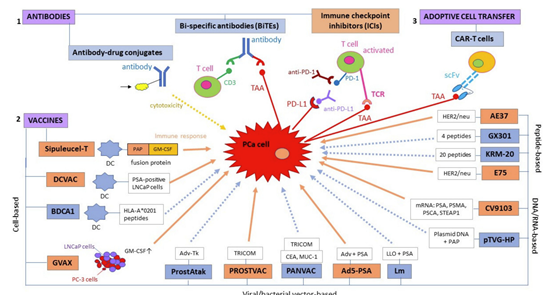
Immunotherapeutic strategies for prostate cancer fall into three main categories: (1) antibodies, (2) vaccines, and (3) adoptive cell transfer; these can be subdivided into smaller categories depending on the mode of action. Immunotherapeutic modalities in orange boxes represent strategies that have been shown to confer a survival advantage to prostate cancer (PCa) patients, whereas immunotherapies in blue boxes are either in pre-clinical/early clinical development or they have so far failed to demonstrate a survival benefit in terms of progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS).
Similarly, orange arrows represent an immune response, whereas dotted blue arrows represent a possible but not yet confirmed immune response. Ad5: adenovirus type 5; AdV-tk: adenoviral vector containing a herpes virus-derived thymidine-kinase; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; DC: dendritic cell; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HLA: human leukocyte antigen; Lm: listeria monocytogenes; LLO: listeria monocytogenes (Lm)-listeriolysin O; LNCaP: lymph node-derived human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line; MUC-1: mucin-1; PAP: prostatic acid phosphatase; PC-3: prostate cancer cell line derived from bone metastasis; PD-1: programmed death receptor-1; PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1; PSCA: prostate stem cell antigen; PSMA: prostate-specific membrane antigen; scFv: single chain variable fragment; STEAP: six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate; TRICOM: TRIad of Co-stimulatory Molecules (Pharmacol Ther. 2021)
Related publications
- Adamaki M, Zoumpourlis V. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 6;13(2):173
- Adamaki M, Zoumpourlis V. Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jun 23;107932
Supporting Grant: NEOVIOPRO: EPAnEK 2014-2020 Operational Programme “RESEARCH CREATE-INNOVATE” (Duration: 31/7/2018-30/1/2022).