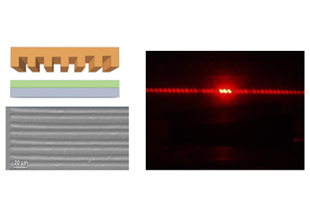
Coupling the sensing and monitoring flexibility offered by photonics technologies, with the data transmission flexibility and wireless networking capabilities provides opportunities to develop hybrid wireless sensor solutions for wireless condition monitoring architectures and maintenance management & support strategies. Use of Plastic Optical Fibers-POF in combination with laser based rapid prototyping and novel functional nanostructured materials is proposed as a viable approach for developing an integrated customizable photonics platform of low circuitry complexity and cost, combining desired characteristics such as reliability, operational autonomy and safe operation in presence of high electromagnetic fields or even in potentially explosive/flammable environments.
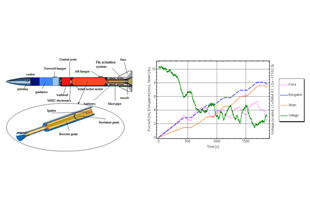
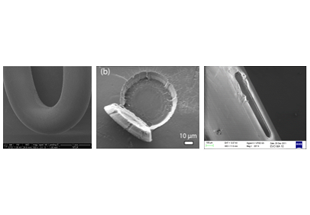
Successful customization has demonstrated efficient, robust sensors for demanding applications like strain monitoring of energetic propellant materials used in solid rocket motors -SRMs for guided or space missiles. Also there have been implemented displacement and strain sensors and systems in heavy machinery production lines and infrastructures.
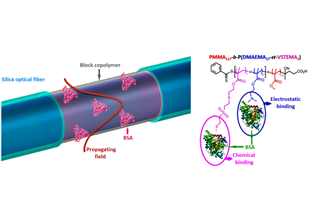
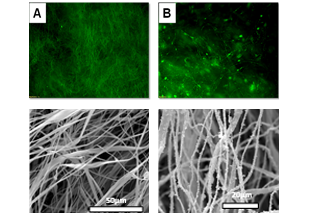
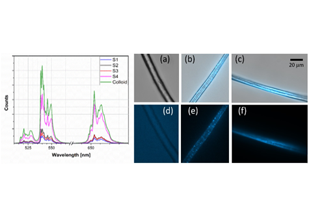
Sensors' customization by proper functionalization of POFs' surface with novel diblock amphiphilic polymers leaded to multiagent sensors allowing the detection of a wide variety of measurands, like toxic aromatic hydrocarbons- benzene and toluene, ammonia, relative humidity levels and specific proteins such as lysozyme or BSA, which find applications in industrial or environmental monitoring and chemical and food industry. Wireless enabled sensors have been demonstrated also for efficient biochemical monitoring of industrial-grade lubricants/coolants' aging in metal polishing/finishing heavy machines with great-anticipated personnel health protection and economic impact.
Key publications